Jonathan Müller
An (In-)Complete Guide to C++ Object Lifetimes
#1about 3 minutes
Defining objects and lifetimes in C++
An object is a region of storage with a type and value, and its lifetime is a property on the abstract machine that dictates when it can be safely manipulated.
#2about 5 minutes
Creating objects with variable declarations and storage duration
Objects created by variable definitions have their lifetime influenced by their storage duration (automatic, static, or thread), which is distinct from the object's actual lifetime that begins after initialization.
#3about 5 minutes
Understanding temporary objects and lifetime extension rules
Temporary objects are created for prvalues and are usually destroyed at the end of an expression, but their lifetime can be extended when bound directly to a reference or used in a range-based for loop.
#4about 5 minutes
Manually creating objects in existing memory with placement new
Placement `new` allows constructing an object in pre-allocated storage, and if the new object is "transparently replaceable," existing pointers and references to the old object remain valid.
#5about 2 minutes
Using std::launder for non-transparent object replacement
When an object replacement is not transparent (e.g., for `const` objects), `std::launder` must be used on old pointers to prevent undefined behavior by forcing the compiler to acknowledge the new object in that storage.
#6about 5 minutes
Implicit object creation and std::start_lifetime_as
Certain operations like `malloc` can implicitly create objects to make C-style code valid, and `std::start_lifetime_as` should be used to correctly begin the lifetime of an object in a raw byte buffer.
#7about 2 minutes
Implicit destruction and best practices for object lifetime
Reusing storage with placement `new` implicitly destroys the previous object, and best practices include explicit object creation and using the newly returned pointer to avoid aliasing issues.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
Matching moments

07:25 MIN
Core design principles and the language evolution trilemma
The Design and Evolution of C++
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in
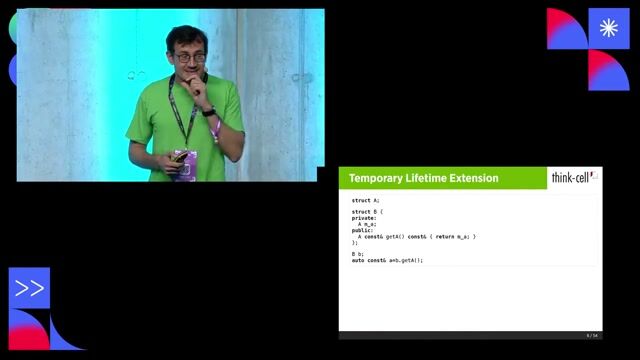
06:01 MIN
Why temporary lifetime extension fails in modern C++
The C++ rvalue lifetime disaster
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in

06:50 MIN
C++ availability, ecosystem, and backwards compatibility
101 brilliant things of C++
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in

03:21 MIN
The dual role of rvalue references in C++
The C++ rvalue lifetime disaster
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in
03:44 MIN
How Java and Go emerged to address C++ limitations
Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Programming Language
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in
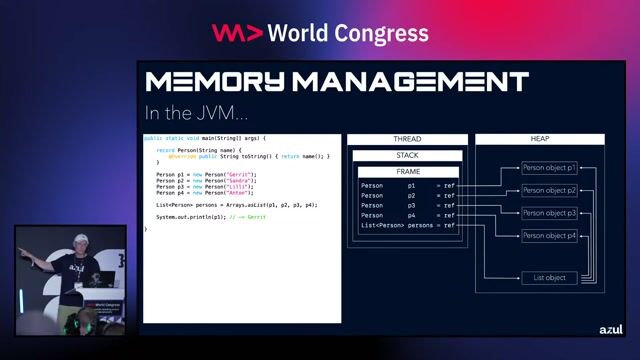
01:19 MIN
How objects become garbage through reachability
Trash Talk - Exploring the memory management in the JVM
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in
02:20 MIN
Understanding the original design goals and evolution of C++
Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Programming Language
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in

02:59 MIN
Practical mitigations for rvalue lifetime issues today
The C++ rvalue lifetime disaster
Unlock Moments
Create a free account to watch a limited number of Moments each month.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
Upgrade to PRO for unlimited access to the full archive.
You have an account? Log in
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 24:17
24:17The C++ rvalue lifetime disaster
Arno Schoedl
 24:13
24:13C++ Features You Might Not Know
Jonathan Müller
 45:27
45:27101 brilliant things of C++
Andreas Fertig
 1:01:15
1:01:15The Design and Evolution of C++
Bjarne Stroustrup
 1:00:16
1:00:16C++ in constrained environments
Bjarne Stroustrup
 26:12
26:12Why Iterators Got It All Wrong — and what we should use instead
Arno Schödl
 00:18
00:18Guided Memory Management: Rust's Ownership Model
Stefan Baumgartner
 25:29
25:29Python: Behind the Scenes
Diana Gastrin
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.


Vesterling Consulting GmbH
€50-60K
UML
Software Architecture

Vesterling Consulting GmbH
€50-60K
UML
Software Architecture





